We are excited to share that our latest research has been published in Scientific Reports, titled "Translational approach for dementia subtype classification using convolutional neural network based on EEG connectome dynamics" (Full text).
This would not have been possible without the dedicated efforts of our team. We extend our deepest thanks to Thawirasm Jungrungrueang, Sawrawit Chairat, Kasidach Rasitanon, Praopim Limsakul, and Krit Charupanit for their contributions throughout this project.
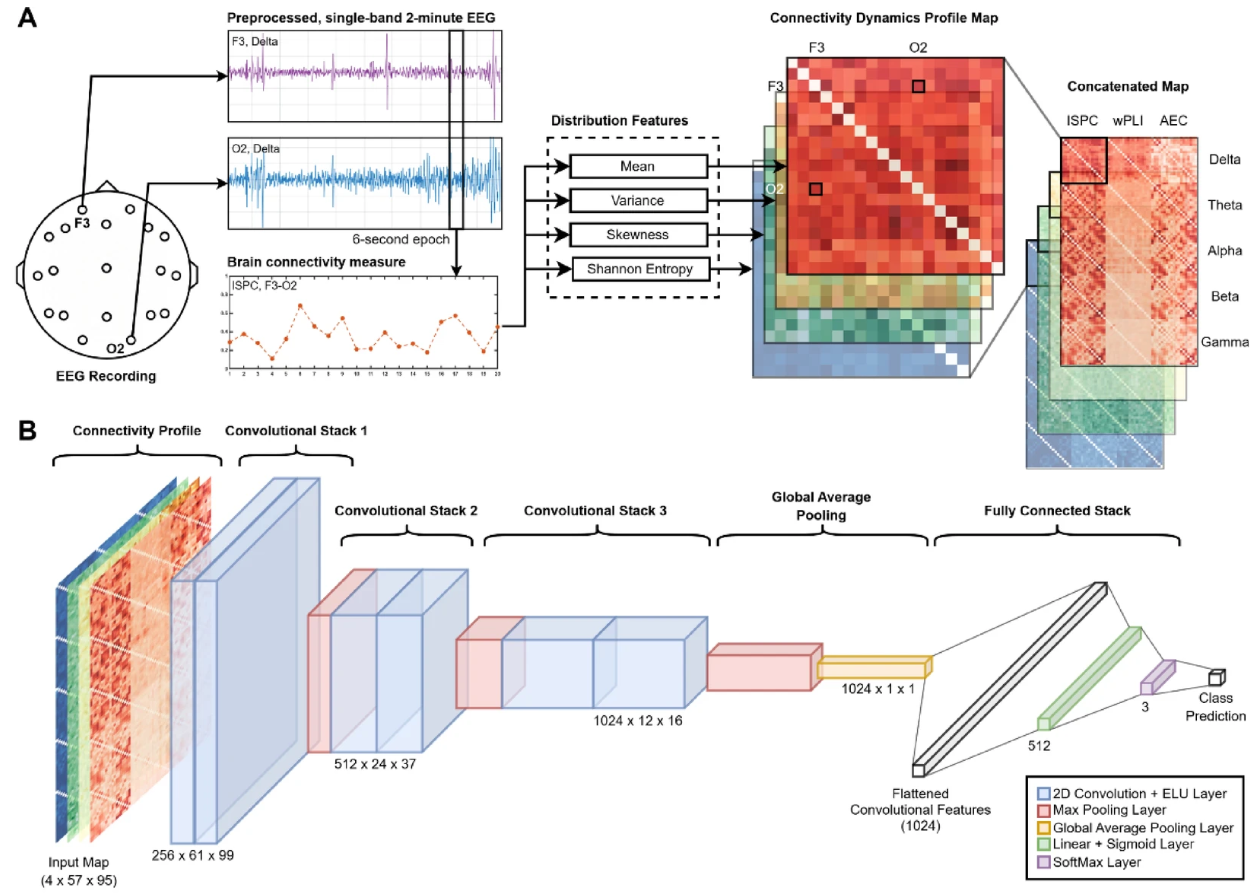
Summary of the Study: Dementia spectrum disorders—most notably Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and frontotemporal dementia (FD)—represent a major global health challenge, with early diagnosis being crucial for effective intervention. In this study, we explored dynamic features of resting-state EEG functional connectivity to uncover subtype-specific brain network patterns. By extracting statistical descriptors such as mean, variance, skewness, and Shannon entropy from connectivity data, we observed generalized Alpha-band connectivity disruptions common to dementia. AD cases displayed widespread Delta-band hyperconnectivity and increased complexity, while FD showed marked disruptions in phase-based connectivity across Theta, Beta, and Gamma bands.
To translate these findings into clinical utility, we implemented a convolutional neural network enhanced with these dynamic features. The model achieved impressive classification performance:
93.6% multiclass accuracy across AD, FD, and healthy controls.
97.8% accuracy distinguishing AD from healthy controls
96.7% accuracy for FD vs. healthy controls
97.4% accuracy in differentiating AD from FD
This research demonstrates the powerful potential of dynamic EEG connectivity as a non-invasive, cost-effective biomarker for early dementia diagnosis. The integration of advanced machine learning with EEG features offers a scalable solution for differentiating dementia subtypes, which is critical for tailored treatments and improving patient outcomes. Beyond classification, our findings open new avenues for using brain network dynamics to track disease progression and personalize therapeutic strategies. We believe this work is a significant step toward making EEG-based dementia screening more accessible, accurate, and informative.
Stay tuned as we continue to explore innovative ways to harness neurotechnology for brain health.